How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly in demand. This guide provides a structured approach, from understanding basic drone components to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to crucial safety regulations. We’ll cover pre-flight checks, essential controls, camera operation, troubleshooting common issues, and responsible drone ownership. Whether you’re a beginner taking your first flight or looking to refine existing skills, this comprehensive resource will empower you to confidently navigate the exciting world of drone piloting.
Understanding the intricacies of drone operation is crucial for both safe and successful flights. This guide breaks down the process into manageable steps, covering everything from pre-flight preparations to advanced maneuvers and post-flight maintenance. We aim to equip you with the knowledge and confidence to handle your drone responsibly and enjoy the many possibilities it offers.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and learn how to safely and effectively control your aircraft.
Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both personal safety and the safety of others.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality. This section details the major components and their functions, along with a comparison of different types of propellers and batteries.
Drone Component Functions

A typical drone comprises several key components working in concert. These include propellers, motors, a flight controller, a battery, a GPS module, and a camera.
- Propellers: Generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, hover, and maneuver.
- Motors: Spin the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, receiving input from sensors and controlling motor speed to maintain stability and execute commands.
- Battery: Provides power to all drone components. Flight time is directly dependent on battery capacity.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Enables precise location tracking, crucial for autonomous flight and return-to-home functions.
- Camera: Captures aerial photos and videos, varying in resolution and features depending on the drone model.
Drone Propeller Types, How to operate a drone
Different propeller designs impact flight performance. Factors such as pitch, diameter, and material affect thrust, speed, and efficiency. Common types include:
- Standard Propellers: Offer a balance of thrust and speed, suitable for general flight.
- Slow-Spin Propellers: Generate higher thrust at lower speeds, ideal for lifting heavier payloads.
- Fast-Spin Propellers: Designed for higher speeds and agility, but may reduce flight time.
The choice of propeller depends on the specific application and the drone’s capabilities.
Drone Battery Types
Various battery types power drones, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are the most common due to their high energy density. However, other types like Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) are gaining popularity.
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Typical Flight Time (minutes) | Weight (grams) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo | 11.1 – 22.2 | 15-30 (varies greatly depending on drone and load) | 100-500+ |
| LiFePO4 | 12.8 | 15-25 (varies greatly depending on drone and load) | 150-600+ |
Note: Flight times are estimates and depend heavily on drone model, payload, and flight conditions.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and successful drone operation. This involves both a visual inspection and functional checks to ensure everything is working correctly and the flight will be safe.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, perform the following checks:
- Inspect propellers for damage or cracks.
- Check motor mounts for tightness.
- Verify battery charge level.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check GPS signal strength.
- Review the weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation).
- Confirm that the flight area is clear of obstacles and within legal airspace restrictions.
- Power on the drone and controller, ensuring a proper connection.
- Run a pre-flight calibration routine (if available on your drone model).
Compass and IMU Calibration
Calibrating the compass and IMU is crucial for accurate flight and stability. The compass determines the drone’s orientation, while the IMU measures acceleration and rotation. Incorrect calibration can lead to erratic flight or crashes.
Visual Inspection
A visual inspection is necessary to identify any potential issues before taking off. Check for loose screws, damaged components, or any signs of wear and tear.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are critical for avoiding accidents. Proper throttle control, orientation, and location selection are essential elements.
Safe Takeoff Procedures
Follow these steps for a safe takeoff:
- Ensure the drone is in a clear, level area, away from obstacles and people.
- Power on the drone and controller, establishing a stable connection.
- Carefully apply throttle, smoothly lifting the drone vertically.
- Maintain a steady ascent, keeping the drone level and stable.
- Once at a safe altitude, begin your flight maneuvers.
Landing Techniques
Landing requires a controlled descent and gentle placement on the ground. Emergency landing procedures should be practiced in a safe environment.
- Normal Landing: Slowly decrease throttle, maintaining a stable descent.
- Emergency Landing: If the drone loses control or encounters an issue, prioritize a safe landing, even if it means a less precise landing.
Takeoff and Landing Location Selection
Choosing an appropriate takeoff and landing location is paramount. Factors such as wind conditions, terrain, and obstacles must be considered.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the drone’s flight controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the control sticks and basic maneuvers.
Flight Control Stick Functions
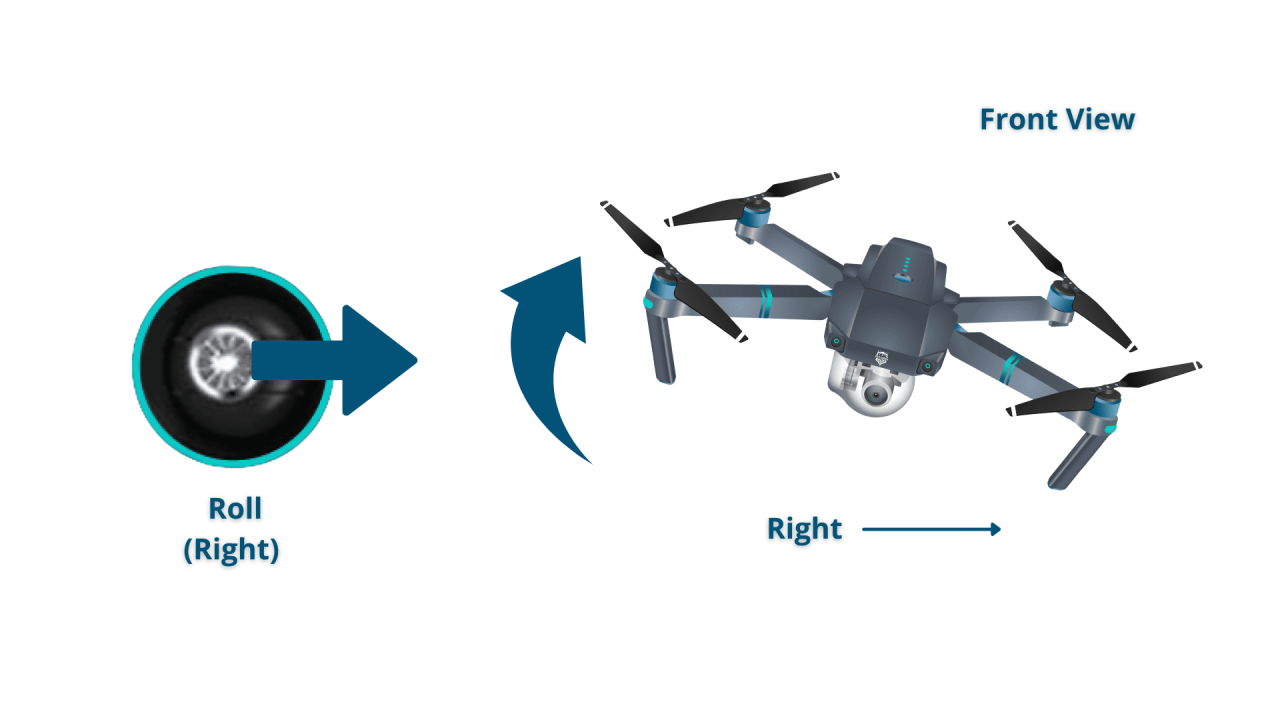
Most drones use two control sticks: one for pitch and roll, the other for yaw and throttle.
- Left Stick (Pitch/Roll): Controls the drone’s movement forward/backward (pitch) and left/right (roll).
- Right Stick (Yaw/Throttle): Controls the drone’s rotation (yaw) and altitude (throttle).
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Mastering basic maneuvers is essential for confident drone operation.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude using the throttle.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude using the throttle.
- Turning: Rotating the drone using the yaw control.
Simple Flight Pattern
A simple flight pattern could involve ascending to a predetermined altitude, hovering for a few seconds, then performing a slow 360-degree turn before descending back to the ground.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Beyond basic maneuvers, advanced flight techniques offer increased capabilities and creative possibilities. However, these techniques require more skill and careful consideration of safety.
Waypoint Navigation and Autonomous Flight
Waypoint navigation allows pre-programming a flight path, enabling the drone to autonomously follow a set of coordinates. Autonomous flight features vary widely across drone models.
Challenges and Safety Considerations in Complex Environments
Flying in complex environments like urban areas or near obstacles presents challenges. Maintaining line of sight, avoiding collisions, and understanding airspace restrictions are crucial.
Flight Modes
Different drones offer various flight modes, such as GPS mode, attitude mode, and manual mode. Understanding these modes is essential for adapting to various flight situations.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture: How To Operate A Drone
The drone’s camera is a key feature, offering unique perspectives for photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and techniques can significantly enhance image quality.
Camera Settings Adjustment
Adjusting camera settings like shutter speed, aperture, and ISO allows for control over exposure, depth of field, and image sharpness.
Camera Modes
Different camera modes offer various creative options.
- Photo Mode: Captures still images.
- Video Mode: Records moving footage.
- Timelapse Mode: Creates a sequence of images over time, compressed into a short video.
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Photography and Videography
Capturing stunning aerial footage requires attention to detail.
- Plan your shots and consider the composition.
- Use the “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
- Maintain a steady flight to avoid shaky footage.
- Edit your photos and videos to enhance their quality.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and responsible drone operation is crucial. This includes adhering to safety guidelines and respecting airspace regulations.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable experience.
Safety Considerations
Always prioritize safety when operating a drone.
- Maintain visual line of sight.
- Avoid flying near obstacles or people.
- Be aware of airspace restrictions and regulations.
- Check weather conditions before flying.
- Never fly beyond your skill level.
Drone Regulations and Laws
Drone regulations vary by location. It’s essential to research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your area before flying.
Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation contributes to a safe and enjoyable flying environment for everyone.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Despite careful preparation, issues can arise during drone operation. Understanding common problems and troubleshooting steps is essential.
Common Drone Problems
Some frequent problems include low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor malfunctions.
Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting steps vary depending on the specific problem, but often involve checking connections, replacing components, or recalibrating systems.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, high power consumption | Charge battery, reduce flight time, reduce payload |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructed signal, interference | Fly in open area, check GPS settings |
| Motor Malfunction | Motor damage, loose connection | Inspect motor, check connections, replace if necessary |
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage extend the lifespan of your drone and ensure optimal performance.
Regular Maintenance Schedule

Regular maintenance includes cleaning, inspecting components, and replacing worn parts. A schedule should be developed based on usage frequency.
Proper Storage Techniques
Store the drone in a clean, dry place, away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight. Use a protective case or bag to prevent damage.
Safe Battery Storage and Charging
Store batteries separately from the drone, in a cool, dry place. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging.
Mastering drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and practice. By understanding the fundamental principles of flight, adhering to safety guidelines, and consistently practicing the techniques Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently and safely explore the aerial world. Remember that responsible drone ownership extends beyond personal enjoyment; it involves respecting airspace regulations, protecting the environment, and ensuring the safety of others.
Safe flying!
FAQ
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions. Research models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved locations or experienced magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal?
If you lose GPS signal, immediately switch to manual mode and carefully bring the drone down to a safe landing. Prioritize maintaining visual line of sight.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, battery capacity, and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
Where can I find information about local drone regulations?
Check your local government’s aviation authority website or the website of your country’s civil aviation authority for information on drone regulations in your area.
